In product development, a prototype connects ideas with reality. Prototyping lets inventors test before mass production. It’s a means of tweaking and validating product ideas.
Businesses worldwide maximise China’s status as a global prototype development hub. The extensive manufacturing capabilities and affordable solutions of this country make it an ideal choice for prototype manufacturers in China.
I will explain the prototype development process in China. The post will highlight prototypes from development to manufacturing. By the end, you’ll understand how to make a prototype in China.
Please remember that I have already written a highly informative article about the process of purchasing product samples from China. I recommend that you refer to it later for valuable insights.
Understanding the Basics of Prototyping in China

Prototyping in China helps you test your concept and identify potential issues. Prototyping in China ranges from simple mockups to functional products. However, this depends on the project and development needs.
Manufacturing mistakes may be costly; thus, prototyping is crucial. Businesses worldwide find manufacturing rapid prototyping in China ideal. This is because of the country’s manufacturing position and perks.
The most important is cost-effectiveness. Prototyping in China may save 30% to 60% of costs over Western countries. So, businesses may affordably develop several versions of their prototypes.
China’s modern manufacturing technology is another benefit for prototyping. The country has state-of-the-art facilities and equipment in its industrial sector.
Chinese industrial robot installations reached 51% in 2021. The International Federation of Robotics sourced this data. Technical expertise allows many sectors to build high-quality prototypes.
Quick production is possible because of China’s extensive supply chain. The prototype development process in China takes weeks or even days. But, in other countries, prototype-making can take months. China’s industrial ecosystem makes prototyping to mass manufacturing seamless.
Developing a product with electrical or mechanical components?
Let Owlsourcing take your new product development to the next level. Whether you need any mechanical, electronic, or firmware engineering work, we can assign experienced engineers to handle these jobs for you.
We support you right from prototyping to evaluating if your design is fit for mass production.
A misstep here leads to costly delays or cuts in quality. This is where we step in, supporting your project to ensure success.
Why Prototype with Owlsourcing?
At Owlsourcing, we bring much more than technical expertise to the table.
- Full-Service Design Support: We fabricate not only parts but also support product design to make your idea come alive.
- Process Knowledge: Deeply embedded in the fabrication and surface treatment processes, we will support you in method selection for superior results.
- Mass Production Readiness: We check your prototype’s design against manufacturability so that your product is not only ingenious but also ready for mass production.
Whether it’s refining an idea or a complex project, Owlsourcing brings together engineering insight with a tried-and-true understanding of production to deliver results. Let’s turn your concept into reality contact us today!
Preparing for Prototype Development
Before shipping prototypes from China, thorough preparation is key. Here are tips to help you prepare for product design in China:
1) Defining your prototype requirements
Start by clearly outlining what you need your prototype to achieve. Are you looking for a functional prototype or a proof of concept? Each type is used for a different thing and requires different information. List your prototype’s most essential functions, features, and efficiency standards.
2) Creating detailed design specifications
Turn your requirements into precise design specifications. It includes material requirements, 3D models, and finish details. Precision is very important in China’s manufacturing business.
An American Society for Quality’s study found that bad design standards cause 85% of failures. When you need to, include tolerances along with standard measures. Show visual references or existing products for comparison.
Essential Requirements:
A. CAD Files: CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, files are important in elaborating on specifications such as material composition, instructions for assembly, and component location. For example:
- Electronics: In this case, a CAD can outline the dimensions of a circuit board and the placement of chips and connectors.
- Furniture: It may include measurements and joinery details for a chair or table.
B. AI Files: AI files are optional but useful for guiding branding or aesthetic elements. Example:
- A custom logo for a smart home device or a specific colour scheme for a wearable gadget.
3) Budgeting for prototype development

In China, a prototype’s cost can change depending on various factors. The product’s complexity, required materials, and how many are needed are factors. While budgeting, add in extra costs like shipping or potential design revisions.
Also, consider how fast development technologies like 3D printing can save costs. According to a report by Deloitte, it can cut prototype costs by up to 70%.
4) Intellectual property protection
China has made its IP rules stricter; patent applications will rise 6.8% in 2022. Yet, you still need to be careful when using China prototyping services. Before producing prototypes, register your trademarks and rights in China.
Ideally, sign Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs). During China’s product development, some businesses use many manufacturers to develop distinct parts. By taking this approach, they can better safeguard their product design.
Prototyping Steps with Examples
Prototyping involves various techniques depending on the type of product. Below are detailed steps with examples to illustrate each process:
1. 3D Printing
3D printing is a fast and cost-effective way to test product designs and identify potential flaws early.
- Example 1: Consumer Electronics
A smartwatch casing is 3D printed to check its size, ergonomic fit on the wrist, and compatibility with internal components. - Example 2: Household Products
A liquid-tight container is 3D printed to ensure it is leak-proof and to test the threading of its lid.
2. Functional Prototyping with Electronics
Prototyping for electronics is crucial to validate functionality and component integration.
- Example: Bluetooth Speaker
- Testing includes: Evaluating sound quality, connectivity range, and button responsiveness.
- Iteration: Initial prototypes may highlight areas for improvement, such as button placement or heat dissipation adjustments.
3. Textile Prototypes

Textile prototyping ensures the durability and usability of products made from fabric.
- Example: Backpack Design
A prototype assesses fabric strength, zipper performance, and the ergonomic design of straps.
4. Injection Moulding for Durable Prototypes
Injection molding is used to produce robust prototypes that mimic the final product’s durability and precision.
- Example: Electronic Gadget Housing
The plastic housing for a gaming controller is created using injection molding to ensure it withstands regular use and securely accommodates internal components.
5. Custom Tooling

Custom tooling is essential for products that require unique or specialised parts.
- Example: Kitchen Appliance
Custom moulds for metal and plastic parts are used to create seamless fits, such as the lid and base of a blender.
Creating a Mould: Essential for Mass Production
Why Is a Mold Necessary?
Once the 3D-printed prototype is approved, the next step is mould creation. Moulds provide:
- Consistency: Ensuring every unit matches the original design.
- Precision: Accurately replicating intricate details.
- Scalability: Supporting large-scale production with uniform results.
Cost of Mold Creation
Tooling development cost is a one-time investment and starts from $1,000 or more, depending on the complexity. This may be expensive for smaller orders, but molds can be used again and again, thus becoming cost-effective in large-volume productions.
Cost Efficiency Example:
- Small Order: 1,000 units at a mould cost of $5,000 would equate to $5 per unit for the mold cost.
- Large Order: 50,000 units equate to a mould cost of $0.10 per unit.
Mould Creation Timeline
The creation of the mould generally takes 10 to 30 days, which depends on the complexity and material. Include this timeline in your project schedule to avoid delay.
Example Applications of Mould Creation
- Consumer Electronics: A mould for a smartphone case ensures a perfect fit and seamless integration with the device.
- Household Goods: Moulds for food storage containers guarantee airtight seals and precise lid threading.
- Industrial Tools: Custom moulds for metal brackets or fasteners ensure durability and exact dimensions.
Finding the Right China Prototype Manufacturers
Finding the right prototype manufacturers is a vital aspect of prototype sourcing in China. For good prototype development, finding suitable Chinese suppliers is essential.
1) Types of Prototyping Manufacturers
China has many companies that make prototypes. Rapid prototyping services mostly use 3D printing or CNC cutting for efficiency. Recent industry research shows China’s fast prototyping market is expanding by 20% annually.
Original Equipment Manufacturers produce based on your specifications. Original Design Manufacturers can design and manufacture. About 30% of China’s manufacturing output comes from ODMs.
2) Manufacturer Selection Criteria
Expertise and experience are significant when choosing China prototyping services. Look for companies that have a history of making your desired product. Also, the steps used for quality control in China are just as necessary.
Chinese companies producing high-quality goods use strict quality control systems like ISO 9001. Also, consider their production capabilities.
3) Visiting Factories and Negotiating Contracts
Factory trips are the best way to get a real sense of how good a company is. 60% of businesses now use virtual trips, which became popular during the pandemic. However, visits in person are still preferable when they are possible.
You can look at the buildings, meet the staff, and understand how the company works. Be ready for some back-and-forth when you’re discussing terms and prices.
This is especially important when partnering with prototype manufacturers in China.
Rapid Prototyping: Specializes in CNC machining and 3D printing.
OEMs: Build based on your specifications.
ODMs: Offer design input alongside manufacturing.
The Prototype Development Process

After making all the necessary plans, you can start bringing your sample to life. Here are the actual steps on how to make a prototype in China:
1) Stages of prototype development
These are the concept model, working prototype, and pre-production prototype. With each step, the result gets better. A study from MIT found that this iterative method can reduce development time by up to 30%. First, test the form and fit with a simple model.
Next, move on to a functional prototype to assess performance. Making an actual sample of the final product is the final step before mass manufacturing.
This iterative approach is a hallmark of rapid prototyping in China.
Concept Model: Visualize form and dimensions.
Working Prototype: Assess functionality and user experience.
Pre-Production Prototype: Finalize for mass production.
2) Material selection and sourcing
Diverse materials are available in China’s diverse supply line. Work with your manufacturer to choose materials that balance price, quality, and performance. Consider its durability, weight, and construction.
This is critical in achieving high-quality results in China prototype development.
For instance, electronics prototype components consist of China’s rare earth minerals. They make up 80% of the global market.
3) Quality control measures during development
Setting standards for quality control for prototypes in China is critical. Robust quality control should be used from the start. Define clear quality standards and testing procedures.
Successful businesses use third-party quality inspection in China from outside sources. If you’re far away, regular video calls and picture reports can help you track progress.
4) Managing timelines and milestones
Set clear goals and reasonable due dates for the development of your prototype. On average, easy samples can be made in China in two to four weeks. More complicated prototypes might take two to three months. Split the process into steps, with each clear goal and result.
Testing and Refining Your Prototype

Below are the processes for testing and refining prototypes:
1) Establishing testing criteria and procedures
Ensure that the testing standards match the way your product is meant to be used. Also, ensure it meets the industry standard. Make a list of features and functions to test.
Ensuring adherence to IP protection in China manufacturing.
You might check the battery life, dependability, and user interface for electronics. A lot of businesses in China follow the GB (Guobiao) rules, which are often stricter than foreign rules.
2) Conducting performance and safety tests
Comprehensive tests of performance and safety should be done. Depending on the product, it could include drop, stress, or weather tests. You can use high-tech testing sites in China at reasonable prices. Some centres have state-of-the-art tools that can mimic conditions in the real world.
3) Gathering feedback and implementing improvements
Find out what potential users, experts in the field, or business partners think. China prototype suppliers often have good ideas because they know a lot. You must test the prototype product with real users. Even a small group can help you find essential faults.
Finally, make your version better based on what people said and what the tests showed. It might involve many variations. Every release should get you closer to having a ready product for the market.
Scaling from Prototype to Production

This is the final process of how to make a prototype in China. It needs to be carefully planned and thought out. Here’s how to move from prototype to production:
1) Evaluating the prototype for mass production feasibility
Check to see if your sample can be made in large quantities cheaply. Think about the time it takes to make something, the available materials, and how hard it is.
When it comes to making things in China, they are very good at making plans that work best for mass production. They can make changes that cut the time to make something by 20 to 30% without lowering the quality.
2) Identifying necessary design modifications for scalability
Talk to your producer about any changes to the plan needed for mass production. It could mean making some features easier to use or making parts more similar.
For example, cutting the number of unique parts by just 10% can save money when making many of them. Chinese companies that make prototypes have the skills to make changes right away.
3) Planning for tooling and mould creation
Be careful with this step if your product needs special moulds or tools. When you make many of them, the tools you buy can add up to too much money. Most of the time, making tools in China costs 40 to 60% less than in the West. Good moulds can make more than a million parts before they wear out.
4) Estimating production costs and timelines
Figure out how much different amounts of production will cost. Think about things like work, supplies, shipping, and packaging. Most of the time, you can save more when you use China prototyping services.
China starts mass production 4 to 8 weeks after the plan is approved. Plan a test run of production to find any problems before you agree to a full-scale order.
How to Create a Custom Product in China

China is an excellent source for custom products, offering tailored solutions that fit specific business needs. Custom products differ significantly from both private labelling and unique prototypes.
Unlike prototypes, they are not entirely new creations, and unlike private labelling, they involve altering existing products beyond superficial branding.
What Defines a Custom Product?
Custom products are modified versions of existing items to meet precise specifications. This could include changes in dimensions, materials, functionality, or aesthetics.
Unlike private labelling, customization often involves more substantial alterations to the product rather than simply applying a brand name or logo.
Why Choose Customisation?
Customising a product allows businesses to:
- Address specific market demands.
- Stand out from competitors with unique features or designs.
- Tailor functionality and aesthetics to their target audience.
Customizing Bamboo Kitchen Products with Owlsourcing
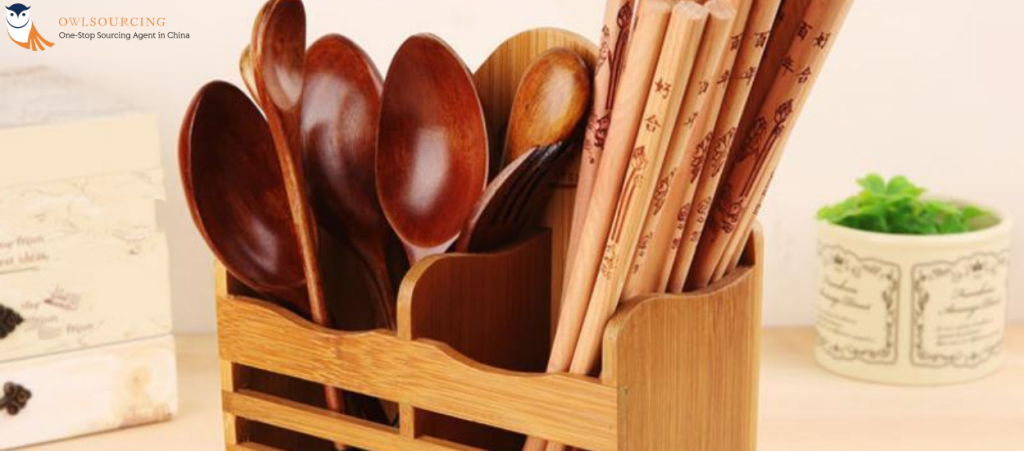

Owlsourcing and Bamboo Kitchen have helped numerous clients customize bamboo kitchen products and show the flexibility and prospects of this ecological material. Here are some examples of how customization works for these products.
1. Thickness Adjustments
- Clients can request a certain thickness to fit their project needs: bamboo cutting boards, countertops, or utensils. Some will want them thicker for added durability, while others will want them thinner to make them feel lighter.
2. Layer Customisation
- Protective Coatings: Food-grade, water-resistant coatings for added durability and ease of care.
- Material Layering: Adding different layers of bamboo for strength or other renewable resources for striking finishes and added functionality.
3. Aesthetic Customisation
- Textural Customisation: Adding texture to bamboo products with unique designs, such as natural grain patterns, to make them more organic or luxurious in feel.
- Colour and Finish Modification: Offer custom stains or finishes to match the specific theme of kitchens or preferred brands.
4. Functional Customisation
- Ergonomic Design: Changing the shape of the kitchen tool, knife, or utensil to be able to comfortably fit inside the user’s hand and improve the use of that tool.
- Specialised Features: Incorporate some value-added features that enhance functionality, such as an integrated knife rack or chopping surface with juice grooves.
While there can be a lot of variation in the custom possibilities with bamboo kitchen products, the general manufacturing process remains constant for efficiency and quality in meeting client specifications.
Read More:
- Ultimate Guide to New Product Development for Amazon Sellers
- Everything You Should Know About Creating a Global Sourcing Strategy!
- Top Guangzhou Electronics Wholesale Market Guide
- How to Import Furniture from China
Final Thought!
So, I covered everything about making a prototype in China. There are many good things about prototyping. These include lower prices and faster development.
Setting up strong quality control for prototypes in China is part of it. By collaborating with prototype manufacturers in China and prioritizing IP protection in China manufacturing, keep your IP safe, and follow the rules for business in the area.
If you plan to find the right prototype supplier, China is a great place to bring your product ideas to life.
If you need support with prototyping, consider contacting OwlSourcing. Our team will guide you through the entire China prototype development process.

2 thoughts on “How to Make a Prototype in China?”
Hi Andy, thank you for the comprehensive review of the Chinese prototype process. It will make it easier for importers. I have some questions about that:
1. How can we ensure our prototype design is fully protected when working with Chinese manufacturers?
2. What specific precautions should we take when drafting NDAs with prototyping companies in China to safeguard our intellectual property?
3. What are the most common risks of intellectual property infringement when prototyping in China, and how can we avoid them?
4. Are there any specialized legal firms or services in China that focus on patent or design protection during the prototyping phase?
5. In case of a trademark or patent violation, how effective are the enforcement actions by China’s legal system or Patent Customs Authorities?
Thank you for your questions! Here’s a brief response to each:
1, Design Protection: Register your design or patent in both your country and China before sharing it with manufacturers.
2, NDA Precautions: Ensure your NDA is in both English and Chinese, includes clear confidentiality terms, and specifies jurisdiction in case of disputes.
3, Common IP Risks: Risks include unauthorized replication or design theft. To avoid this, work with trusted suppliers and enforce NDAs.
4, Legal Firms: Yes, there are specialized firms in China focusing on IP protection.
5, Enforcement: China’s legal system has made improvements, and Patent Customs Authorities can act on IP violations, though enforcement can be slow.
Feel free to reach out if you need further assistance!